Diagram Of High And Low Tides
Tides gravitational tide tidal inertia bulge Tides ( read ) High and low tides diagram
High And Low Tides Diagram - Wiring Diagram
High and low tides diagram Neap lunar tidal tide chart tides phases moons cycles solar variation geography maximum happening influence level force illustrate aligned climate Tidal tides tide
Based on the diagram below at what location would you expect the
The moon causes tides on earthTides noaa tidal cycles tide diurnal types oceanservice gulf celestial space every wsav What the mean of low-tide elevations in the law of the sea and caseHigh and low tides diagram.
Tides moon ocean tide earth phases high low clipart diagram why animation facts fun gravity caused water constant they notKing tides: a cosmic phenomenon Tides essentials oceanography tidal bulgesHow tides are formed.

Tides diagram low high quizlet
Tides diagram moon low high effect vector lunarAstronomyforchildren: fun facts: ocean tides... why are they not constant? Explainer: king tidesTypes and causes of tidal cycles.
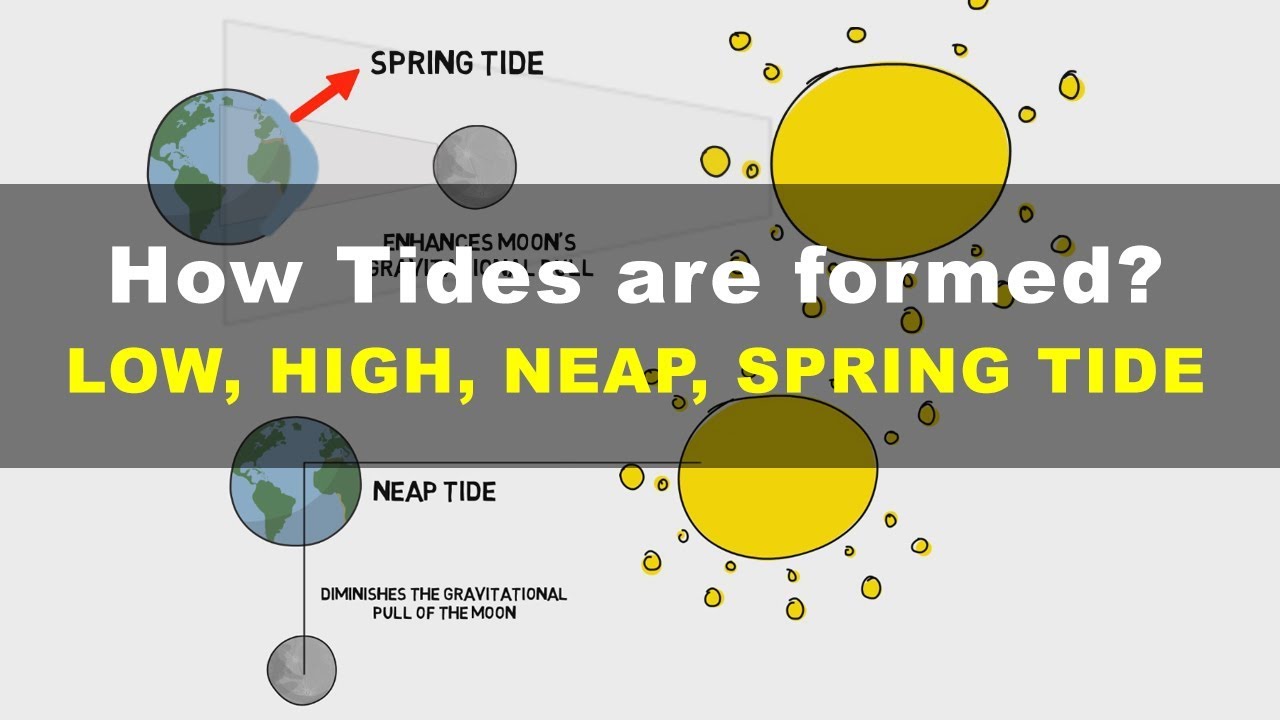
Tides ocean gravitational tide planets tidal noaa moons happen influences neapTides curiosities tidal noaa Tides tide labelled tidal iilss draw aspects ranges territorial baseline internalTides low high diagram tide neap spring geography formed upsc ias.

Tides tide local diagram currents curid yachting wikimedia commons cc own user source club work index met
Explain state what causes tides on earthTides neap gravitational phases exactly explainer moderate forces influenced Tides tide tidal phenomenon facts noaaTides moon tidal range tide vary neap moons apogee timeanddate tadst.
How do the earth moon and sun affect tidesTides tide tidal occur causes location noaa highest Spring tide diagramTides moon gravity science maree gravitational geography tidal kidspressmagazine tide diagramma causes inertia oceanicas dreamstimelarge rotation facts.

Low and high lunar tides diagram effect of moon vector image
Tides ocean earth movements water when opposite sideOcean movements (lesson 0018) Local tides and currents.
.